The Medical Diagnosis
In medicine, diagnosis (plural, diagnoses) is a tag given for a medical state or disease identified by its signs, symptoms, and from the results of various diagnostic events. The term "diagnostic criteria" designates the combination of signs, symptoms, and test results that allows the clinician to establish the diagnosis of the respective disease.
However, it has two distinct dictionary definitions. The first definition is "the recognition of a disease or state by its outward signs and symptoms," while the second definition is "the analysis of the causal physiological/biochemical cause(s) of a disease or condition."
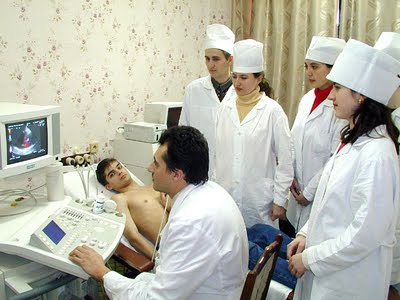
Typically, a person with abnormal symptoms will consult a health care provider such as a physician, podiatrist, nurse practitioner, physical therapist or physician's assistant, who will then obtain a medical history of the patient's illness and perform a physical examination for signs of disease. The provider will formulate a hypothesis of likely diagnoses and in many cases will obtain further testing to confirm or clarify the diagnosis before providing treatment.
Medical tests frequently performed are measuring blood pressure, checking the pulse rate, listening to the heart with a stethoscope, urine tests, fecal tests, saliva tests, blood tests, medical imaging, electrocardiogram, hydrogen breath test and occasionally biopsy.
For instance, a common disorder such as pneumonia was nevertheless used as a diagnosis before the germ theory was accepted, and the disease was defined as a complex of many symptoms consisting of cough, sputum production, fever and chills. Later, as the actual cause was assigned to micro-organisms, the term diagnosis included the causality, e.g., pneumococcal pneumonia, suggesting not only a spectrum of symptoms but also a cause for the symptoms.

0 Comments:
Post a Comment
<< Home